Environmental electrochemical Sensing 环境传感技术
Electrochemical Environmental Sensing
Advanced detection technology is the prerequisite of efficient environmental protection and pollution control. Fast, highly sensitive detection technology can not only protect the health of the public, but also of some significance for the study of impact of environmental pollutants exposure on human health. At present, domestic and international relevant environmental monitoring technology is often related to bulky and expensive analyzing equipment. These complicated techniques are often time-consuming, expensive and are difficult to achieve real-time monitoring. Therefore, it is of great importance to develop a simple, rapid and high sensitive detection technology for the timely and accurate understanding of the situation of environmental pollution, and to develop a comprehensive and reasonable environmental protection scheme.
· Electrochemical sensing
Compared with the existing environmental testing technology, electrochemical sensing technology processes great advantage in basic research on mechanism of chemical reactions and analytical application. It can be carried out to directly study the interaction mechanism of environmental pollutants and reacting agents, to clarify the mechanism of environmental pollution detection, and to optimize the detection condition based on its intrinsic properties, reduce the reaction time, and ultimately achieve rapid and highly sensitive detection of a target material. Therefore, owning to its miniaturization, fast, accurate, convenient, real-time and continuous detection capability, electrochemical sensor has great application prospect for continuous monitoring of environmental pollution.
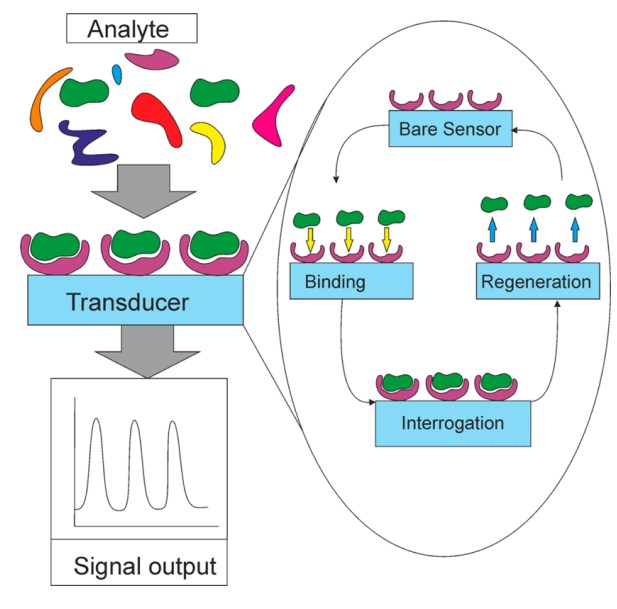
Fig 1. Working principle of electrochemical biosensors.
· Bioelectrochemical system (BES) based sensing technique
At the present stage, it is difficult to realize real-time monitoring and early warning for the detection of toxic substances in water body by using non in-situ chemical means due to its poor timeliness. Besides, most of the technology are expensive and need external power supply. In recent years, microbial fuel cell (MFCs), as a new type of environmental “shock” sensor that combines the biosensing and electrochemical technology, has cast light on the ideas of on-line monitoring of wastewater quality. Bio-toxic substances in wastewater can directly inhibit the anodic exoelectrogenic bacteria activity in MFC, which thus realizes the real-time monitoring of toxic substances through the plummeted electrical signal output. Compared with the traditional biological sensor, as an environmental toxicants “shocks” early warning technology, MFC has the advantages of rapid response, simple structure, low cost and sustainable self-powering. The FunMat group will focus on improving the limit of detection (LOD) and sensitivity of the MFC based “shock” biosensor, as well as shortening the system start-up time.
· Microfluidic environmental sensors
During the past few years, a growing number of groups have recognized the utility of microfluidic devices for environmental analysis. Microfluidic devices offer a number of advantages and are ideally suited to environmental analyses in many respects. Environmental monitoring faces many challenges, including the ability to handle complex and highly variable sample matrices, which provide the incentive for continuous research. Additionally, the need to operate for days to months in the field requires further development of robust, integrated microfluidic systems. Microfluidic devices offer a number of advantages, including rapid detection and identification of compounds, low sample and reagent consumption, and the potential for field monitoring. The high demands on microfluidic ingenuity stem from the complexity and diversity of environmental sample matrices and the broad classifications of contaminant. Here in our group, we are currently working on developing microfluidic sensors for water quality detection as well as contamination sensing, providing the next generation integrated portable sensors for environmental monitoring.
电化学环境传感
先进的检测技术是保护环境、控制污染的首先条件,快速、高灵敏的检测技术不仅可以保障公众身体安全,同时对于研究环境污染物暴露对人群健康的影响也 具有重要意义。目前,国内外相关环境检测技术往往涉及到大型的检测设备,但是这些技术存在前处理复杂、耗时、仪器价格昂贵、难以进行实时监测、或不够灵 敏、检测限很高的问题。因此,开发简单、快速、高灵敏的新型检测技术对及时、准确了解环境污染状况,制定全面、合理的保护方案具有重要意义。
· 电化学传感
电 化学传感器作为一种在基础化学机理研究和分析应用中有巨大优势的技术,与已有成熟的环境检测技术相比,它有着得天独厚的优势: 它可以直接进行环境污染物与作用物之间的相互作用机制的研究、阐明环境污染物检测机理,从根源上优化检测条件、节省反应时间,最终达到快速、高灵敏检测目 标物质的目的。因此,电化学传感器以其微型化、快速、准确、便捷、可实时和连续检测等特有优势,成为具有极大的实际应用前景的环境传感技术。

Fig 1. Working principle of electrochemical biosensors.
· 微生物电化学传感
现 阶段对水体环境毒性物质进行的检测多采用非原位化学手段,时效性较差,成本高,需额外提供电源,难以实现实时监测预警。近年来,微生物燃料电池 (Microbial fuel cells, MFCs)作为一种将生物传感与电化学技术相结合的新型环境毒性“震动”传感器,为污水水质的在线监测提供了新的思路。废水中毒性物质可直接抑制MFC毒 性传感器阳极产电菌活性,从而通过其电信号输出的骤减实现对毒性物质的实时监测。相对于传统生物传感器,MFC毒性传感器作为市政及工业废水环境毒性物质 的“震动”预警技术,具有反应迅速、结构简单、成本低廉和自我供能等优点。
然而,由于MFC阳极产电菌驯化时间较长,在经过大剂量毒性物质 刺激之后,需较长时间恢复传感性能,从而制约了MFC毒性传感器的实际应用。此外,当MFC阳极产电菌在较长时间内不断受到某种特定毒性物质刺激,优势菌 种将得到自然筛选,产电菌群将建立起相应抗性,进而影响MFC毒性传感器传感性能(检测限、灵敏度)。课题组将围绕以上问题展开研究。
· 微型环境传感器
过 去的几年里,一部分研究团队认识到可以将微流控器件应用到环境分析上来。微流控器件在环境分析的多个方面具有明显优势,是一种理想的选择。环境监测面临的 诸多挑战,例如处理复杂多变的多个环境样品,促使该领域不断向前发展。再者,原位环境监测要求传感装置在数天乃至数月的时间内稳定运行,因此对系统的稳健 性以及集成性提出了要求。微流控器件具有多方面优势,包括快速检测与识别化合物,只需消耗极少量的环境样品及反应试剂,为原位监测提供了便利。环境样品的 复杂性以及多样性使得微流控器件中的微流控特征成为极大的优势。Funmat课题组目前致力于研发基于微流控传感器的水污染检测技术,为下一代集成可携带 传感器在环境监测中的应用提供技术支持。

